Lesson 3: Calculation A – Movement of Policies
Understand MOP Components
MOP explains how a policy “behaves” during its entire policy life cycle, i.e. from setting in force to termination (claims / surrender / maturity):
- When a policy is in force, the insurance fund administering the policy receives premiums and pays for expenses (i.e. General Administration Expense (“GAE”) and Agency Related Expense (“ARE”)) and commissions to the distribution channels acquiring the policy, such as tied agent, broker and banks.
- When a policy is terminated, the insurance fund pays relevant benefits (claim / lapse / maturity) to the respective beneficiary eligible for the termination event. No cash flow should occur after the termination.
In Malaysia, insurance / takaful companies are required to MOP statistics to the regulator, i.e. Form L6, L7 & L8 for conventional life insurance and FT5, FT6 & FT7 for family takaful.
Timing of Event Occurrences

For the purpose of actuarial modeling, we assume policy movements occur either at the beginning or end of the month .
- Beginning of month (“BOM”): New business and maturity.
- End of the month (“EOM”): Death, total & permanent disability (“TPD”), critical illness (“CI”), lapse.
Many insurance products covers (1) death & TPD; or (2) death, TPD & CI at the same time, namely claim benefit is payable when one of the eligible events occurs. For such products, TPD & CI are considered as accelerated benefits (which accelerate benefit amount payable on death).
- In actual practice, benefit amount payable TPD / CI may be less than death benefit – especially if the responsible underwriter views the life insured is too risky for full TPD coverage, or the accumulated TPD benefits exceed the limit accepted by the insurance company.
- For example, a policy may pay 100,000 upon death but only 75,000 upon TPD. The policy shall continue to remain in force until death or maturity – if death occurs before the policy matures, the remaining benefit of 25,000 is payable and the policy is terminated.
- For the purpose of actuarial modeling, we assume accelerated benefits are the same as death benefits and the policy shall be terminated upon one of the eligible events.
- Maturity does not require any assumptions as it is equal to the no. of in force policies as at the end of the last policy month.
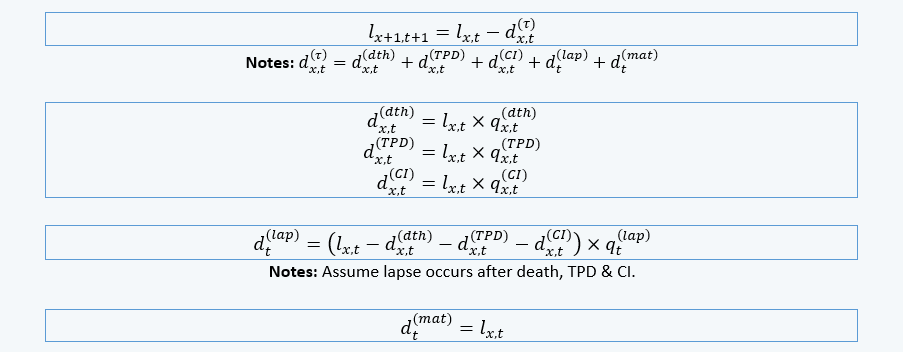
MOP Formulas
The following formulas are used to calculate MOP components:
Further Reading
Additional reading for the concepts of preparing statistical analysis on movement of policies: